
It is difficult to imagine living today without being connected to computer networks, email, distance education, the cloud, and in the electrical world, SCADA systems, local networks in substations, connections and management of equipment remotely, and a endless services that we use every day. However, the greater the diversification, the greater the security control over […]
It is difficult to imagine living today without being connected to computer networks, email, distance education, the cloud, and in the electrical world, SCADA systems, local networks in substations, connections and management of equipment remotely, and a endless services that we use every day. However, the greater the diversification, the greater the security control over these must be. In the 1940s, to destroy a country’s economy it was necessary to have weapons and large amounts of money that could finance such an attack. Currently, with computer networks, which are accessible at very low costs, it is possible to economically destabilize a country by attacking its critical infrastructures. To fully understand what this implies, it is necessary to understand what a threat means, where it originates and what are the measures and / or recommendations to take.
Threats
A threat is understood as any risk factor likely to materialize to the detriment of a company, city or nation. Now, any computer threat embodied in the electricity system can have a great negative impact, compromising the electricity supply in Bolivia, and may even at some point be classified as terrorism or attacks on national security.

Attacks on critical infrastructures is not something new, among the most notorious cases are:
- Stuxnet: In 2010, a very sophisticated “computer worm” took control of 1000 machines that participated in the production of nuclear materials and whose objective was the self-destruction of the same. This virus was developed since 2005.
- Black Energy: This Trojan had its beginnings of development in 2007 and was improved until its attack on plants in Ukraine (Dec 2015), achieving a blackout. This attack was based on the Spear Phishing technique, which uses emails making their origin appear to be true, they include Excel and Word documents with macros in charge of infecting computers on the destination network.
- ndustroyer: (December – 2016), is a virus oriented exclusively to critical systems, it looks for known vulnerabilities in Siemens and GE equipment and is capable of controlling the switches of a substation directly.
- Brazil (April 29, 2020): The Energisa group suffers a hacker attack, the objective, to encrypt the servers, and request a “ransom” of R $ 5 million.
- United States (May 2021): The Colonial Pipeline company, one of the largest transporters of gasoline, diesel and fuel using a pipeline system, was forced to shut down its systems due to a cyberattack. The company paid $ 4 million as a ransom.
- United States (June 2021): The meat processing company JBS was forced to paralyze its operations in the United States and Australia as a result of a cyber attack (ransomware). The company paid $ 11 million as a ransom. The FBI considered this attack one of the most sophisticated.
Who are behind an attack
The idea that young and rebellious people are behind such a sophisticated attack as those mentioned is far from reality.
We find criminal companies, which are very well organized, hierarchical and have a classic internal structure, like that of any company.

They have many specialized engineers, in charge of carrying out very sophisticated attacks, they have large budgets, they plan and prepare their attack in several years and they are always in continuous learning, seeing new techniques and attack methodologies, looking for vulnerabilities to enter and carry out a massive contagion.
They are industries specialized by product and service lines, with specialties in:
- Malware (Malicious Software whose objective is to infiltrate the device without our knowledge)
- Intrusion, money laundering and mule networks, which consist of opening bank accounts using stolen identities, or offering “easy” money in exchange for allowing us to use our bank account and carry out transactions on our behalf. Santander Bank of Spain closes approximately 12,000 “mule accounts” per year
The objectives pursued by this type of company are mainly:
- Profit through information theft, hijacking, Ransomware and its demand for ransom
- Disruption of Services
- Fraud
- Attack critical infrastructures, seeking as much damage as possible

Action
We are faced with the so-called endless race of “the sword and the shield.” The attackers discover the sword and we discover the shield, they discover the gunpowder and we discover the bulletproof vest. The advancement of attack and defense techniques happens very quickly, vulnerabilities are discovered in a short time and it is for this reason that many systems are continually updated, contrary to what happens in electrical systems, due to the very particular behavior that have.
A substation equipment to be implemented to state subjected to a series of tests under a certain Hardware and Software that guarantee its operation. Updating these computers may result in previously tested software not working properly with new updates.
To think that with the purchase of some security devices we are safe is unreal, since there is no 100% secure system.
Security-conscious companies invest a lot of money in implementing mechanisms to protect themselves, and continuously train their staff in specialized security topics, since this area is very large.
The main objective is to protect the integrity and availability of systems and networks, hardware and software, data and information. This is achievable through procedures, products, and people.
Risk management seeks within these objectives the development of contingency plans based on a risk analysis either to cancel or mitigate the probability of success of a threat, and in the event that it occurs, control its impact.
The application of world-known safety models and guides helps in this end. One of them is defense in depth, which among its guidelines has:
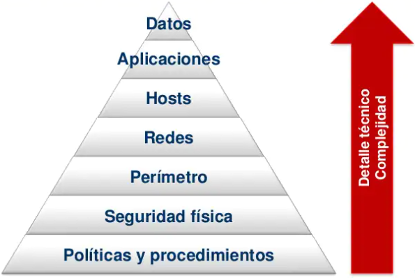
- Control of physical access to facilities
- Physical segmentation of the IT network and the OT network where equipment is installed
- Fraud
- Creation of DMZ (demilitarized) zones to isolate critical systems into protected segments
- Implement industrial firewalls by placing them at the perimeters of the IT network, substations and critical systems
- Secure remote access (VPN)
- Centralized administration and management
Strategic companies are the most vulnerable to cyber attacks, since due to the type of activity they carry out, they merit the implementation of a more specific cybersecurity scheme.
The incorporation of security policies must be part of the quality processes of the companies. As well as obtaining international certifications of cybersecurity infrastructure based on standards such as NERC-SIP, taking into account the IEC64351 recommendations and without leaving aside the formation of Security Operation Centers (SOC) that must be made up of interdisciplinary staff.
The awareness, socialization and continuous training of the personnel of the Bolivian electricity sector, on security policies and the proper use of the networks will help in this objective.
Current Ende Transmission Policy
Ende Transmisión, aware of these challenges, carries out through its qualified personnel the management, acquisition and implementation of state-of-the-art security equipment in order to reduce the possible risk of an attack that could compromise its facilities and its SCADA system.
He also actively participates in seminars and courses related to cybersecurity of critical systems to keep up-to-date on this topic.
It works together with the SIEMENS company (SCADA system provider) updating the base software (currently in the process of applying the version 3 update package) in order to achieve greater stability and security in your system.









